- HOME
- Products
- HPLC Columns
- Chiral CD-Ph
A Chiral column for chiral separation with silica-based phenylcarbamated β-cyclodextrin as the chiral selector.
For those looking to achieve chiral separation of racemic mixture with a structure comprising benzene rings, we provide sufficient retention with phenylcarbamate and excellent selectivity with β-cyclodextrin.
Are you worried about finding a Chiral column that hits your enantiomers target?
The Chiral CD-Ph column presents "Phenyl carbamated β-cyclodextrin" as a functional group. The outstanding retention made possible with phenyl
carbamate and the excellent selectivity made possible with β-cyclodextrin raise the hit rate of your samples.
If your samples contain a benzene ring, and if they are basic and/or neutral compounds, the Chiral CD-Ph may be just what need for chiral separation.
Features
Certainly retained and separated with Phenyl carbamated β-cyclodextrin
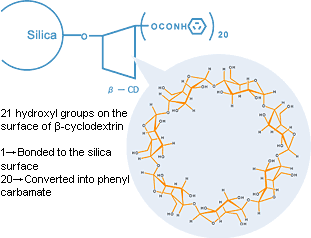
Chiral CD-Ph is packing material for chiral separation created from a precisely classified high-purity spherical silica with phenyl carbamate beta-cyclodextrin chemically bonded as a chiral selector.
The balance between the hydrophobicity and polarity of phenylcarbamate assures sample retention, and the central cavity of β-cyclodextrin presents excellent chiral recognition with inclusion.
Excellent chiral selectivity
Chiral CD-Ph excels at the chiral separation of basic and neutral compounds.
Applications of chiral separation
Separation Factors (α) on Columns (Osaka Soda) for Optical Separation
| Compound | Column* | α | Temp | Eluent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral Compound | ||||
| Bendroflumethiazide | CD | 2.40 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=2/8 |
| Benzoin methyl ether | CD | 1.12 | 25°C | i-C3H7OH/n-C6H14 =2.5/95.5 |
| 1-(4-Bromophenoxy)-1-ethoxyetane | CD | 1.17 | 25°C | H2O/CH3OH=3/7 |
| 2-Bromo-1-phenylpropane | CD | 1.03 | 25°C | H2O/CH3OH=4/6 |
| 2-Bromo-N-phenylpropionamide | CD | 1.12 | 25°C | C2H5OH/n-C6H14=1/9 |
| Carvone | CD | 1.14 | 25°C | H2O/CH3OH=3/7 |
| 2,4-Dichloro-α-methylbenzyl alcohol | CD | 1.05 | 25°C | H2O/CH3OH=1/1 |
| 2,2-Dimethyl-1-phenyl-1-propane | CD | 1.03 | 25°C | H2O/CH3CN=6/4 |
| 1,2-Epoxy-3-phenoxypropane | CD | 1.11 | 25°C | C2H5OH/n-C6H14=4/6 |
| (2,3-Epoxypropyl)Benzene | CD | 1.22 | 25°C | H2O/CH3OH=3/7 |
| Flavanone | CD | 1.56 | 25°C | H2O/CH3OH=1/9 |
| Hexobarbital | CD | 1.32 | 25°C | C2H5OH/n-C6H14=4/6 |
| Mandelonitrile | CD | 1.05 | 25°C | C2H5OH/n-C6H14=2/8 |
| 2-Methoxy-2-phenylethanol | CD | 1.17 | 25°C | H2O/C2H5OH=6/4 |
| 1-Phenyl-1,2-ethanediol | CD | 1.11 | 5°C | H2O/CH3OH=6/4 |
| 1-Phenylethanol | CD | 1.10 | 25°C | H2O/CH3CN=6/4 |
| 1-Phenyl-1-propanol | CD | 1.19 | 15°C | H2O/CH3CN=8/2 |
| Triadimefon | CD | 1.03 | 25°C | i-C3H7OH/CH3OH/n-C6H14 =2/15/83 |
| Compound | Column* | α | Temp | Eluent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic compound | ||||
| Alprenolol | CD | 1.30 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=4/6 |
| Atenolol | CD | 1.21 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3OH=1/1 |
| Atropine | CD | 1.10 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=7/3 |
| 4-Chloroamphetamine | CD | 1.86 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3OH=3/7 |
| 2-(Ethylamino)propiophenone | CD | 1.44 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=4/6 |
| Homatropine | CD | 1.05 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=6/4 |
| Isoprotenol | CD | 3.01 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=1/1 |
| α-(Methylaminometyl)benzyl alcohol | CD | 1.49 | 60°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3OH=2/8 |
| 2-(methylamino)propiophenone | CD | 2.29 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3OH=4/6 |
| Metanephrine | CD | 1.08 | 25°C | 20mmol/L KH2PO4/CH3OH=4/6 |
| Metoprolol | CD | 1.15 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=1/1 |
| 1-(1-Naphthyl)ethylamine | CD | 1.26 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=1/1 |
| Nicardipine | CD | 1.13 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=1/1 |
| Norphenylephrine | CD | 2.71 | 25°C | 50mmol/L KH2PO4/CH3OH=2/8 |
| Norepinephrine | CD | 1.36 | 25°C | 50mmol/L KH2PO4/CH3OH=6/4 |
| Oxyphencyclimine | CD | 1.06 | 15°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=6/4 |
| Perhydroindol | CD | 1.08 | 25°C | 20mmol/L KH2PO4/CH3CN=6/4 |
| 1-Phenylethylamine | CD | 1.62 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3OH=4/6 |
| Phenylephrine | CD | 1.89 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3OH=2/8 |
| Pindolol | CD | 1.21 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=1/1 |
| Propranolol | CD | 1.66 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3CN=2/8 |
| Synepherine | CD | 1.84 | 25°C | 0.5mol/L NaClO4/CH3OH=2/8 |
| Tetrahydropapaveroline | CD | 1.96 | 25°C | 50mmol/L KH2PO4/CH3OH=3/7 |
| Thioridazine | CD | 1.10 | 25°C | 20mmol/L KH2PO4/CH3CN=6/4 |
*:CD:Chiral CD-Ph
The list of chiral compounds non- separable with Osaka Soda columns Acephate, Camphorquinone, Catechin, 3,3,3-Trifluoro-2-methoxy-2-phenylpropanenitorile, Pantoyl lactone, 1-Phenoxy-2-propanol, 2-Phenyl-2-butanol,
2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-(9-anthryl)ethanol, Tetrahydro-3-furoic acid, N-Acetylprocainamide, 2-Amino-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanol, 1-Acetoxy-8-hydroxy-1,4,4a,9a-tetrahydroanthraquione, Anabasine, Carbinoxamine, 5-Ethyl-5,6-dihydro-3,8-dinitro-6-phenyl-6-phenanthridinol,
Laudanosoline, Arginine, Histidine, Lysine
Close
Method study according to the customary procedures.
The Chiral CD-Ph column is capable of using mobile phase in normal as well reversed-phase mode. First select the separation mode according to sample solubility.
After this, examine conditions according to the customary procedures.
Flow chart
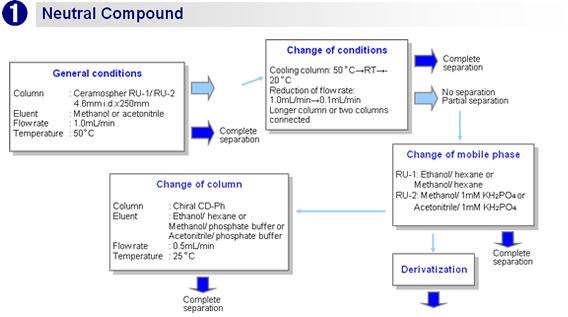
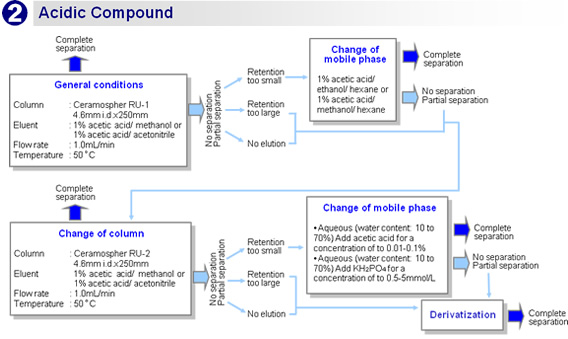
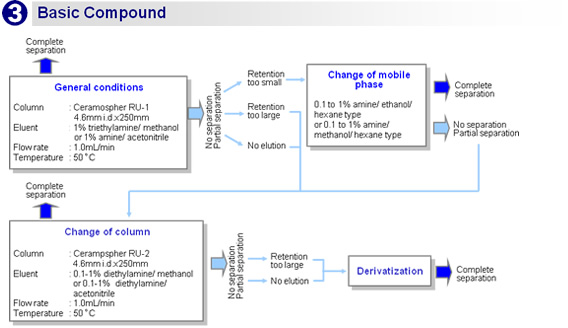
![[Temperature]At a lower temperature, the separation performance is higher, the retention time is longer, and the pressure is higher.[Flow rate] At a lower flow rate, the separation performance is higher but the retention time is longer.[Mobile phase]- Aqueous (reversed phase):Increasing the water content improves the separation performance but increases the retention time, lowers the sensitivity, and raises the pressure.- Hexane (normal phase):Increasing the hexane content improves the separation performance but increases the retention time, lowers the sensitivity, and raises the pressure.](img/ce/ce_00002_05.gif)


Close
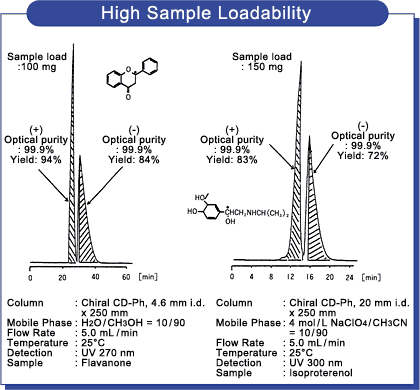
High loadability
As Chiral CD-Ph is capable of processing a high load volume per analysis, efficient preparation is realized.
Moreover, thanks to the use of precisely graded high-purity silica gel, low pressure is also a noteworthy feature. Column sizes
suitable for preparative separation are also available. Chiral CD-Ph provides you extended work from analytical to preparative separation with confidence.
Data 1 :High sample load
Close
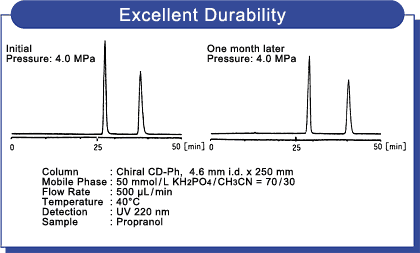
Excellent durability
Chiral CD-Ph's excellent durability provides solid support for long-term R&D projects such as the development of new pharmaceutical products or raw materials.
Data 2 :Excellent durability
Close
Physical properties
| Type | Particle diameter (µm) |
Pore diameter (nm) |
Specific surface area (m 2/g) |
Range of acceptable pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD-Ph | 5 | 8 | 350 | 3.5〜6.5 |

