MG Series (MGIII, MGII, MG) / UG / SG / AG / CR / AQ/ DD/ BB/
UHPLC columns (IF2, IF, MGIII-H, ADME-HR S2)
|
|
CAPCELL is provided with packing material made of totally porous spherical silica coated with a mono-layer silicone-polymer having octadecyl (C
18) as well as other functional groups.
The epoch-making packing material integrates the high separation performance and pressure resistance of silica packing material and the durability of organic polymer-based packing
material.
|
|
1.Handling the Column
|
|
|
|
1.
|
Handle the column with great care. A strong shock may cause damage.
|
|
2.
|
Attach or detach the column when the pressure gage indicates zero.
|
|
3.
|
The maximum column operating pressure is 100 MPa for IF2 and ADME S2, 50 MPa for MGIII-H and BB-H, 40 MPa for IF, and 20 MPa for others.
(*ADME S2 with i.d. 3.0mm: 60MPa)
|
|
|
2.Attaching the Column
|
|
|
|
1.
|
The column joint is of the male nut type for tubing of 1/16 inch OD. Check that the tubing joints of the system fit correctly and that the ferrule tips are deeply inserted into the joints. (See Fig. 1.)
|
|
2.
|
Before attaching the column, replace the liquid in the system with the mobile phase to be used.
Note the replacement procedure to avoid salting out. The shipment solvent is described in the column report enclosed with the column.
|
|
3.
|
Attach the column according to the direction of the arrow.
|
|
|
3.Analysis
|
|
|
3-1.Mobile Phase
|
1.
|
All solvents acceptable for the conventional chemically bonded silica columns can be used.
|
|
2.
|
The applicable pH range for capsule-type packing material depends on the bonding group. The recommended operating pH ranges for Capcell Pak columns are listed in Table 1. The applicable range of pH is determined by operating pH
limits under which the retention and the number of theoretical plate are maintained without decrease. It will vary depending upon the temperature and the concentration of organic solvent. For continued high performance of the
columns, ensure to avoid using pH exceeding the recommended ones. In addition, high temperature and organic solvent-poor condition will result in short column lifetimes when working at the extremes of pH.
|
|
|
Table 1 Applicable pH range for capcell pak columns
|
Bonding group
|
C
18
|
C
8,Phenyl,C
1,CN
|
NH
2
|
C
18+SCX
|
|
Type
|
BB |
ACR
|
UG
|
IF
AQ
SG
|
DD
|
UG
|
SG
|
UG
|
CR
|
|
MG
|
AG
|
SG
|
|
AG
|
|
|
|
Applicable pH
|
1~11
|
1~10
|
2~10
|
2~9
|
1.5~10
|
2~10
|
2~9
|
2~8
|
2~7
|
|
|
|
|
Note: The durability of C
1 and CN column are not comparable with that of C
8 and Phenyl columns because of their short function groups.
|
|
|
 |
|
3.
|
After full degassing, filtrate the mobile phase using a membrane filter 0.45 µm or smaller to remove dust.
|
|
4.
|
A 2-µm filter is used at the column inlet. To prevent foreign matter from clogging the column inlet filter, we recommend using a line filter.
|
|
5.
|
The mobile phase stated in the report is sealed in a new column. To change to a mobile phase containing inorganic salt, note the replacement procedure to avoid the salting out.
|
|
6.
|
Ion-pair reagent will slightly result in short column lifetimes
|
|
7.
|
AQ column is applicable 100% aqueous mobile phase. However, the column lifetime will extremely vary depending upon the HPLC conditions. It is known that acidic phosphate buffer will provide better column lifetimes.
|
|
8.
|
To prevent column deterioration, avoid the following:
·Frequent change of the mobile phase composition
·Rapid change in pressure of column inlet
·Continued using at pressure exceeding 15 MPa
(100 MPa for IF2 and
ADME S2, 60MPa for ADME S2 with i.d. 3.0 mm, 40 MPa for IF, and 50 MPa for MGIII-H and BB-H)
·High column pressure due to the use of a high-viscosity mobile phase
·Prolonged water flow
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
3-2.Preparing a Sample Solution
|
1.
|
Dissolve the sample in a solvent of the same composition as the eluate wherever possible.
|
|
2.
|
Using a solvent with strong dissolving power may lower the separation efficiency or cause the sample to precipitate at the column head.
|
|
3.
|
If there is insoluble matter remaining in the sample solution, filtrate the solution using a filter 0.45 µm or smaller.
|
|
4.
|
The pH of the sample solution should be set in acceptable pH range for packing material.
|
|
|
|
|
|
3-3.Notes on Analysis
Columns of CAPCELL PAK series generally show similar separation profiles to those of corresponding conventional silica-based columns, although slight selectivity difference may be observed depending on the analyte. When optimizing the
conditions for compounds already done with conventional columns, use the same condition as a starting one.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
(1)When using C
18,C
8,Phenyl,C
1,or CN
|
1.
|
Regarding the guard column: Use a column of the same packing material as the main column. If a guard column of different packing material or the chemically bonded silica column of a different manufacturer is used, a separation
profile may not be as expected.
|
|
2.
|
To analyze basic compounds which are protonated under neutral conditions, peak shapes became sharper according to the buffer concentration and amount of organic solvent in mobile phase.
|
|
3.
|
If analysis is performed with a neutral or acidic mobile phase after using a basic or strongly acidic mobile phase, retention times and peak shapes of basic compounds may become unstable.
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
(2)When using NH
2
1.Analysis of carbohydrate
|
|
·
|
Set the mobile phase conditions for a mixed solution of acetonitrile and water. As the acetonitrile concentration is higher, the carbohydrate retention is greater.
|
|
|
·
|
If methanol or buffer solution is used for the eluate, peaks have a tendency to broaden.
|
|
|
·
|
When you try to reproduce the same separation already done with NH
2 columns of other manufactures, raise the acetonitrile content by 5vol% from their conditions.
|
|
|
·
|
Avoid using 100% water in preparing carbohydrate samples. Sample solutions of 100% water deteriorate peak shapes by the nature of normal-phase chromatography. Prepare carbohydrate samples in order to contain acetonitrile for more
than 50%.
|
2.Analysis of ionic substance
|
|
·
|
Set the mobile phase conditions with a well-defined pH value by the use of buffer.
|
|
|
·
|
When optimizing pH, begin with a high pH, then lower it as needed.
Once mobile phase of low pH was used, the surface of packing material will be changed irreversibly.
|
|
|
·
|
It may take a long time (24 hours or more) to equilibrate the column. Since the equilibrating time depends on the flow volume and the salt concentration, allow the mobile phase to remain at a high flow volume or the same pH and high
salt concentration in urgent cases.
|
|
|
·
|
Ascorbic acid may show peak tailing.
|
|
|
·
|
Allantoin does not ionize in the pH range from 2 to 8. However, the use of a phosphate buffer solution is advised.
|
Example of mobile phase: Acetonitrile/water = 80/20, 5 mmol/L KH
2PO
4, pH = 2.0 (H
3PO
4)
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
(3)When using CR
| |
Packing material of CR is a mixture of C
18 and SCX. In ion exchange mode, the following factors will change elution behavior significantly.
|
| |
·
|
pH (pH should ideally be 2.0 or more away from pKa for full ion separation from the sample)
|
| |
·
|
Salt concentration
|
| |
·
|
Amount of organic solvent
|
| |
·
|
Salt type
|
|
|
4.Storing the Column
|
|
|
|
1.
|
Seal the column with the accessory plug and store it in a cold place where there is little temperature fluctuation.
|
|
2.
|
Replace the column with solution of organic solvent and water having the same composition as the mobile phase after using solvents containing strong organic acids such as TFA or basic solvents. (Do not use 100% water.) Moreover,
for storage of one week or longer,replace the column with acetonitrile.
|
|
3.
|
For storage within one month after using, replace the mobile phase with a solution of organic solvent and water having the same composition as the mobile phase and then fill it with the solvent used at the time of shipment. (Refer
to the column report.)
|
|
4.
|
Avoid using 100% water to rinse a column that is other than AQ.
|
|
|
5.End Fittings
|
|
|
|
1.
|
An analytical column of up to 6-mm ID uses a filter-embedded end fitting as shown in Fig. 1. The filter cannot be changed alone. If the filter is clogged or the column pressure is high, replace the end fitting. See Table 3 for the
replacement parts and repair items.
|
|
2.
|
See Fig. 1 for the column connection. If the tubing is inappropriate, especially if a tube for a different type of column is used, the length after the ferrule tip (V in Fig. 1) is often different from the end fitting length L, and
a problem may occur.
If L is greater than V, dead volume may be generated and cause peak broadening or tailing or deterioration of separation performance.
If L is smaller than V, liquid may leak because of inadequate ferrule
adhesion.
Therefore, we recommend replacing the ferrule together with the column.
*If the column is replaced frequently, the male nut may crush the ferrule and liquid may leak. Since tightening the nut too much may cause its head
to come off, replace the ferrule at an early stage.
|
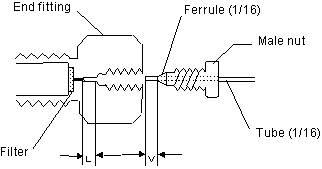
【Fig. 1】 Column connection
|
|
|
|
|
 |
6.Replacement Parts and Repair Items
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3 Replacement parts and repair items
|
Part No.
|
Part Name
|
Description
|
|
21105
|
End fitting (4.6 mm)
|
2 pieces
|
|
21107
|
End fitting (6 mm)
|
2 pieces
|
|
21110
|
Ferrule (1/16)
|
Ferrules (1/16)10pieces
|
|
|
|
|
7.Troubleshooting
|
|
|
Problems in high performance liquid chromatography are attributable to various causes that cannot all be listed up. The table below describes some comparatively common problems related to the column.
|
Symptom
|
Cause
|
Measures
|
|
|
Blocking with foreign matter
|
1.
|
Dust or insoluble matter in the mobile phase or sample solution.
|
|
2.
|
Dirt in the tubing.
|
|
3.
|
Plunger seal fragment.
|
|
4.
|
Precipitation of sample components.
|
|
|
•
|
Sonicate the filter or replace it.
|
|
•
|
Filtrate the mobile phase and sample solution in advance using a membrane filter.
|
|
•
|
Attach a line filter.
|
|
•
|
Clean the tubing and replace the plunger seal.
|
|
•
|
Prepare a sample solution with the mobile phase.
|
|
|
2.
|
Peak splitting, tailing, and broadening.
|
|
|
1.
|
Void in the column head.
|
|
2.
|
Dead volume due to inappropriate connections.
|
|
3.
|
Inappropriate mobile phase conditions.
|
|
•
|
Ion suppression method: Inadequate suppression (Too much sample).
|
|
•
|
Ion-pair method: Inadequate concentration of the ion-pair agent (Too much sample).
|
|
4.
|
Column deterioration.
|
|
*
|
Not repairable in the case of column deterioration or damage to the packing condition.
|
|
|
•
|
Reconnect the tubing.
|
|
•
|
Review the pH, salt concentration, sample amount, and other conditions.
|
|
•
|
Review the ion pair agent concentration, pH, sample amount, and other conditions.
|
|
•
|
Check the column performance using standard inspection solution.
|
|
|
3.
|
Retention time too long or unstable.
|
|
|
1.
|
Liquid leak (Indicated on the pressure gage of the pump).
|
|
2.
|
Inappropriate mobile phase conditions.
|
|
3.
|
Inadequate column equilibration time.
|
|
|
•
|
Check the pump and tubing for any leaks.
|
|
•
|
Secure adequate equilibration time.
|
|
|
4.
|
Retention time too short.
|
|
|
1.
|
Hydrolysis (deterioration) of a bonded groups by strong acid or base.
|
|
2.
|
Inappropriate mobile phase conditions.
|
|
3.
|
Inadequate column equilibration time.
|
|
-
|
•
|
Secure adequate equilibration time.
|
|
|
CAPCELL PAK is shipped after a strict performance check. However, if you should find any defect, please contact your dealer or Osaka Soda for replacement.
Note that Osaka Soda does not warrant the product against column life or deterioration
caused by the failure to follow the above handling instructions.
Ten or more days after reception by the customer, Osaka Soda will assume that the product was delivered in good condition, and will not accept a later replacement
request.
2008 / 10 / 1
2nd edited 2011 / 8 / 1
3rd edited 2015 / 7 / 14
4th edited 2016 / 2 / 29
|
|
|
|
 |


